Solar Power Inverter – Functions, Benefits and Tips
As renewable energy continues to gain momentum worldwide, solar power has emerged as a cornerstone of sustainable living. At the heart of every solar system are photovoltaic (PV) panels, which capture sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. Yet, it is the solar inverter—often called the “brain” of the system—that makes this energy truly usable.
More than just converting DC into alternating current (AC) for homes and businesses, modern inverters play a critical role in optimizing efficiency, ensuring safety, and enabling smart monitoring. Understanding how solar inverters work, the different types available, and the key factors that define a high-quality model is essential before making any solar investment.
1. What Is a Solar Power Inverter? Why Does It Matter?

A solar power inverter (solar inverter) is one of the most essential parts of any photovoltaic (PV) system. In simple terms, it acts as the gateway that turns the raw power generated by solar panels into usable electricity for your home or business. Without it, the energy captured from the sun would remain in a form that appliances cannot consume.
This is why it matters. Direct current (DC) is produced naturally by solar panels, but alternating current (AC) powers the majority of our daily devices and the electrical grid. The primary function of the inverter is to convert DC to AC so that the electricity is safe to export to the utility grid and can be used for office and home appliances. In this sense, the solar inverter serves as a link between the generation of solar energy and actual energy use.
2. Working Principle of Solar Inverters
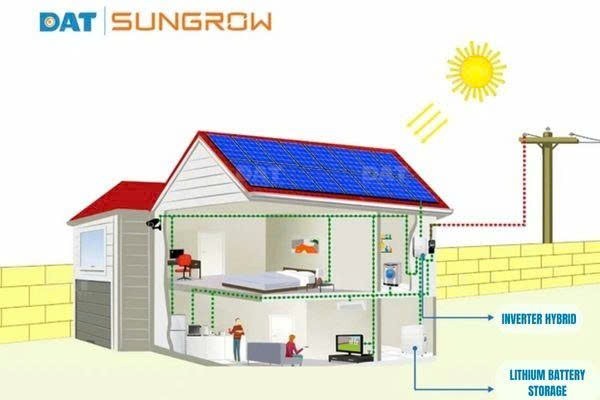
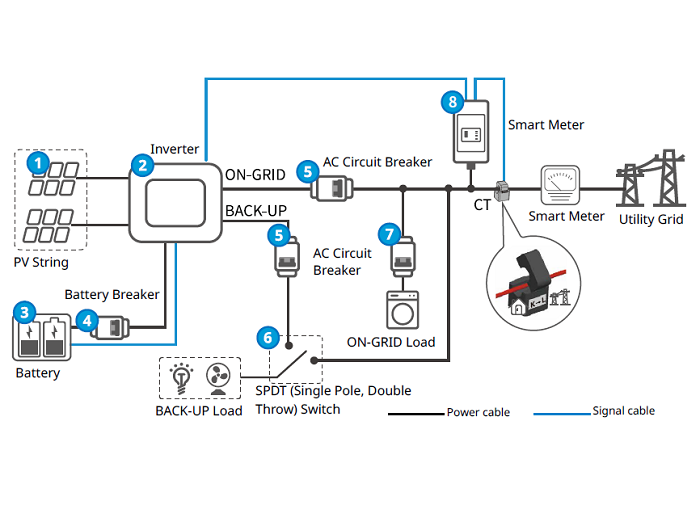
A solar inverter works by converting the variable direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC)—typically 120V or 240V—which is the standard form of electricity used by most home appliances and the utility grid.
Here’s how it happens: sunlight strikes the photovoltaic (PV) cells in your panels, which are made of semiconductor materials like crystalline silicon. These semiconductors consist of positive and negative layers joined by a junction. When photons from sunlight hit the cells, they excite electrons, causing them to move between the layers and create a flow of electricity, known as direct current (DC).
This DC energy can either be stored in a battery for later use or sent straight to the inverter, depending on the design of your system. Once inside the inverter, the current is rapidly switched on and off through transistors, creating a waveform that mimics alternating current. This signal is then passed through a transformer, which adjusts the voltage and produces a clean AC output.
In essence, the inverter acts as the bridge between solar power generation and real-world energy consumption, ensuring that the electricity harvested from the sun can power your home or office or be fed into the grid.
3. What Does a Solar Inverter Do?
Often referred to as the “brains” of a solar energy system, the inverter does far more than just convert electricity. Without it, the entire PV array would remain unable to deliver usable power to your home, business, or the grid. Here are the core functions that highlight why inverters are indispensable:
3.1. Converting DC into AC—the essential role
Solar panels generate direct current (DC), but homes, offices, and the utility grid all operate on alternating current (AC). The inverter bridges this gap, transforming raw solar energy into a usable format that can power everyday appliances or be exported to the grid.
3.2. Maximizing energy harvest with MPPT
Modern inverters use Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) to constantly monitor voltage and current from the panels. This ensures that even when conditions change—such as cloud cover, shading, or natural panel degradation—the system continues to operate at the highest possible efficiency. A well-performing MPPT function can significantly increase overall energy yield across the system’s lifetime.
3.3. Interfacing intelligently with the grid
Smart inverters no longer function as passive devices; they now provide two-way communication with the utility grid. This means they can help regulate voltage, frequency, and reactive power to stabilize the grid. For instance, if there’s a minor disturbance in grid voltage, the inverter can “ride through” the event, assess the situation, and only disconnect if the disturbance persists. This ability enhances both system resilience and grid reliability.
3.4. Monitoring and reporting system performance
Today’s inverters are equipped with advanced connectivity options like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or Bluetooth. Through dedicated apps and web portals, system owners can access real-time data on production, track efficiency trends, and receive error or diagnostic alerts instantly. This visibility not only helps with proactive maintenance but also builds confidence in the investment.
3.5. Ensuring safe operation throughout the system’s lifetime
Safety is paramount, and inverters play a critical role in protecting both equipment and people. They are designed to detect and shut down in the event of arc faults, ground faults, or grid outages, minimizing fire risks and electrical hazards. While not all inverters detect these issues with equal accuracy, leading brands—such as CHINT—are recognized for their robust safety performance and compliance with international standards.
4. Which Types of Solar Inverters Should You Know?
Now that you understand what a solar inverter is and how it works, let’s explore the different types of inverters available. Each has unique advantages and limitations, and the right choice depends on the size of your system, budget, and energy goals.
4.1. String Inverters
- Overview: String inverters are the most common and cost-effective option for residential and small commercial solar installations. Solar panels are wired in series (“strings”) and connected to one central inverter.
- Advantages:
- Affordable upfront cost, making them attractive for budget-conscious homeowners.
- Proven technology with a wide range of brands and models.
- Simple installation and maintenance since there is only one main unit.
- Drawbacks:
- Performance of the entire string can drop if just one panel is shaded or underperforming.
- Less design flexibility for roofs with multiple orientations or complex layouts.
- Best For: Homes with unshaded, simple roof designs and limited budgets.
4.2. Microinverters
- Overview: Microinverters are small devices installed directly under each solar panel. They convert DC to AC at the panel level, allowing every panel to operate independently.
- Advantages:
- Shading on one panel doesn’t affect the performance of the others.
- It’s easier to expand your system later—just add another panel with its own microinverter.
- Panel-level monitoring lets you track the exact performance of each module.
- Drawbacks:
- Higher initial cost compared to string inverters.
- Maintenance may be more complex since the units are located on the roof.
- Best For: Roofs with shading issues, multiple directions, or homeowners who want maximum efficiency and monitoring.
4.3. Hybrid Inverters (Battery-Ready Inverters)
- Overview: Also known as “multi-mode inverters,” these devices not only convert DC to AC but also manage energy storage. They can charge and discharge batteries directly, giving you more control over when to use stored power.
- Advantages:
- Store excess solar energy for use at night or during grid outages.
- Improve energy independence and reduce reliance on the grid.
- Smart energy management for households planning to add batteries in the future.
- Drawbacks:
- More expensive than standard string inverters.
- Installation and system design are more complex.
- Best For: Homeowners who want to combine solar with battery storage or plan to go partially off-grid in the future.
4.4. Central Inverters
- Overview: These are large-scale inverters designed for solar farms and utility-scale projects. Instead of serving one house, a central inverter manages power for hundreds or even thousands of solar panels.
- Advantages:
- Economical for large installations, offering lower cost per watt.
- High efficiency when paired with well-designed solar arrays.
- Drawbacks:
- Not suitable for residential use.
- Require significant space, infrastructure, and cooling systems.
- Best For: Large commercial projects, solar farms, and utility-scale solar power plants.
4.5. Off-Grid (Stand-Alone) Inverters
- Overview: These inverters are built for systems that are not connected to the utility grid. They rely on batteries to supply power at night or during cloudy days, making them essential for remote areas.
- Advantages:
- Provide total energy independence.
- Ideal for locations without reliable grid access.
- Drawbacks:
- Require large, costly battery banks to ensure continuous power supply.
- Maintenance of storage systems can be demanding.
- Best For: Remote properties, cabins, or rural areas where grid connection isn’t available.
5. Tips for choosing the right size inverter
5.1. Match Inverter Capacity to Your Solar Array
Your inverter should be sized to handle the peak output of your solar panels. For example, a 3 kW solar system typically requires a 3 kW inverter. An undersized inverter can waste energy, while an oversized one may be less efficient.
5.2. Think Ahead for System Expansion
If you plan to expand your solar array in the future, consider investing in an inverter that is 20–30% larger than your current solar panel output (a DC/AC ratio of around 1.20–1.30). For example, if your panels currently generate 6 kW, choose an inverter rated at 7.5 kW to 8 kW. This way, you won’t need to replace the inverter later, and your system will be ready to grow with your energy needs.
5.3. Prioritize High Efficiency Ratings
Select an inverter with an efficiency of at least 93% (transformer-based) or 95% (transformerless) if your system will be linked to the grid. For the PV system to use its power as efficiently as possible, these thresholds are essential.
5.4. Get Expert Advice Before You Buy
Every roof, household, and energy profile is different. Consulting a certified solar installer ensures you get the right inverter size and type for your property, maximizing both performance and long-term savings.
6. Where to Install a Solar Inverter
Selecting the right spot for your solar inverter is about balancing practicality, safety, and efficiency. A well-chosen location can enhance performance and extend the lifespan of your solar system. Below are five of the most common and effective places for inverter installation, along with their benefits and key considerations.
6.1. Inside a Garage or Shed (Most Popular)
Garages and sheds are among the most popular installation sites for grid-tied inverters. These areas provide protection from harsh weather and are usually located close to the main electrical service panel, which helps reduce cabling distance and energy losses.
The main drawback is that garages and sheds can become very hot in summer. To prevent overheating, ensure there is sufficient ventilation. Installing a simple thermometer or adding cooling fans can help maintain an optimal operating temperature.
6.2. In a Utility Room
Another excellent option is placing the inverter in a utility room, such as a laundry or service room. This location is typically near the main electrical panel, which simplifies installation and minimizes energy loss. Utility rooms also provide shelter from direct sunlight, high humidity, and extreme temperatures.
For best results, make sure the room has proper airflow or ventilation fans. Leave adequate space around the unit for easy maintenance and future servicing.
6.3. Mounted on an Exterior Wall (With Protection)

If an indoor option isn’t possible, installing the inverter on an exterior wall can work well—provided it is properly shielded. Since grid-tied inverters are often designed for outdoor use, they can function safely outdoors if protected from rain, direct sun, and temperature extremes.
Consider installing a shading cover or placing the unit inside a small protective cabinet to safeguard against weather while still allowing ventilation. Mounting the inverter close to the meter box and service panel will also reduce voltage drops and improve efficiency.
6.4. Inside a Separate Utility Cabinet
For larger households, a dedicated outdoor utility cabinet can be an ideal solution. Housing the inverter in a cabinet keeps it away from living spaces while still protecting it from weather, dust, and humidity.
To ensure reliable performance, the cabinet should be ventilated, moisture-resistant, and easily accessible for maintenance. Positioning it in a safe, convenient spot also helps with long-term system upkeep.
6.5. Underneath the House (Queenslander Homes)
For Queenslander-style homes, beneath the house is a practical and efficient installation site. This location provides natural shade, weather protection, and ventilation, helping the inverter operate efficiently without overheating.
It’s important to confirm that the area is dry, well-ventilated, and free from dampness. Accessibility for maintenance should also be factored in when choosing this option.
7. Maintenance Practices and Security Considerations
7.1. Check for Weatherproofing
Make sure your inverter is adequately protected from the elements. If it’s installed outdoors without full coverage, consider investing in a weatherproof enclosure to extend its lifespan and prevent costly damage.
7.2. Monitor the Display Regularly
Keep an eye on the inverter’s display panel. It provides valuable insights such as real-time power output, daily energy production, and lifetime system performance. Regular monitoring helps you spot and address potential issues early.
7.3. Pay Attention to Warranties
A strong warranty gives you peace of mind. Most inverters last 10–25 years, but standard warranties range from 5 to 15 years, with extensions often available for an extra cost. The longer the warranty, the better your protection against unexpected failures.
7.4. Perform Regular Maintenance
Basic upkeep, like gently wiping the inverter with a dry cloth, helps keep dust and debris at bay. Combined with periodic professional servicing, this ensures your inverter operates efficiently throughout its lifetime.
7.5. Schedule Professional Check-Ups
Have a certified technician inspect your inverter at recommended intervals. Professional checkups can identify hidden issues, optimize system performance, and ultimately extend the inverter’s operational life.
8. DAT Group Solutions Solar Electricians
When investing in a solar power system, choosing the right supplier and installer of solar inverters is a decisive factor for the efficiency and longevity of the entire system. DAT Group not only brings you genuine inverters and solar energy equipment but also fully accompanies a team of more than 400 professional and experienced employees.
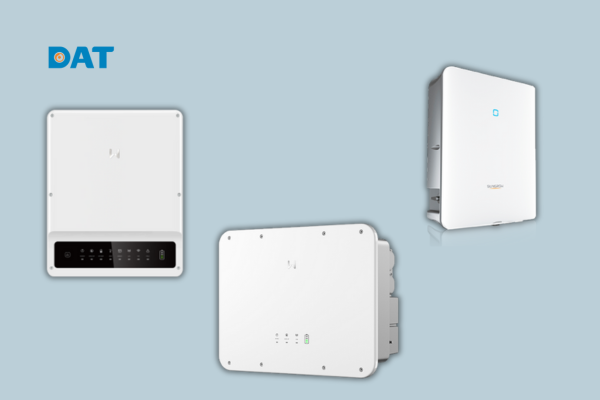
- Genuine, diverse products: We directly distribute inverters, panels, and solar accessories from the world’s leading brands such as SMA, Sungrow, GoodWe, Canadian Solar, and INVT, ensuring superior quality and a genuine warranty.
- Specialized technical team: Our solar power engineers understand every technical detail, helping you optimize the capacity, performance, and durability of the system.
- Consulting suitable solutions: Not only do we sell products, but we also help you choose the inverter and equipment that best suits your needs and budget.
- After-sales support: Maintenance services, operational monitoring, and technical support are always available, giving you peace of mind to maximize the benefits of solar energy.
With DAT Group, you are not just buying a product but also investing in a complete, efficient, and safe solution. Check out a selection of our products:
| Product name | Power rating | Key highlight | Price |
| GoodWe ES Uniq 10 KW (Single-Phase Hybrid) | 10 KW | Hybrid inverter with up to 200% DC input overload; IP65 protection; exclusive distribution by DAT Group; ideal for residential & small commercial systems. | $1,400–$1,700 |
| GoodWe ES Uniq 12 kW (Single-Phase Hybrid) | 12 KW | Expanded capacity; supports parallel operation; enables battery storage and backup loads for enhanced energy security. | $1,600–$1,900 |
| INVT XG 6-10 kW (Three-Phase On-Grid) | 6-10 KW | Mid-range three-phase inverter; multiple MPPT inputs; suitable for small commercial sites or homes with heavy loads. | $1,500–$2,200 |
| INVT XG 110 kW (Three-Phase On-Grid) | 110 KW | Utility-grade inverter engineered for large commercial or industrial solar farms; premium efficiency and reliability | $18,000–$25,000 |
| Sungrow SG5.0RS On-Grid Inverter | 5 KW | High yield with 98.4% efficiency, multiple protection features | $1,100–$1,400 |
| SMA Sunny Tripower 15kW | 15 KW | German technology, proven reliability, integrated grid management | $3,000 – $3,300 |
Choosing the right type of inverter and the most suitable installation location will determine the efficiency and longevity of your solar power system for many years to come. A wise decision is not only about investing in high-quality products but also about partnering with a trusted and professional provider.
DAT Group-Solutions takes pride in being your reliable partner, delivering not only genuine products but also comprehensive solutions from consultation and installation to long-term maintenance. If you’re looking for a solar energy system that is safe, efficient, and cost-effective, we are your number one choice.
Contact DAT Group-Solutions today for expert consultation and take the first step toward a sustainable energy solution for your home or business.