Hướng dẫn xử lý nhanh các sự cố thường gặp của hệ thống hybrid
Với xu hướng sử dụng năng lượng xanh phục vụ cho đời sống và sản xuất, số lượng các hệ thống điện năng lượng mặt trời (NLMT) tại Việt Nam tăng lên rất nhanh. Đã có hàng ngàn hệ thống điện NLMT hòa lưới (On-Grid) và hòa lưới có lưu trữ (Hybrid) được lắp đặt và đưa vào vận hành, giúp người sử dụng tiết kiệm chi phí tiền điện cũng như góp phần làm giảm lượng khí thải CO2.
Trong đó, hệ thống Hybrid có thể lưu trữ lượng điện mặt trời dư vào ban ngày để sử dụng vào buổi tối hoặc khi mất điện. Đồng thời, cung cấp nguồn điện liên tục, ổn định cho các thiết bị điện quan trọng như camera giám sát, tủ lạnh, tủ đông, hệ thống máy tính, wifi, hệ thống báo cháy, cửa cuốn điện, hồ cá Koi… Do đó, rất nhiều gia đình Việt đang có nhu cầu lắp đặt hệ thống Hybrid để sử dụng.
Tuy nhiên, để hệ thống Hybrid vận hành tối ưu và đạt hiệu suất cao, người sử dụng cần nắm rõ nguyên tắc hoạt động và cách xử lý nhanh khi hệ thống gặp phải những lỗi thông dụng.
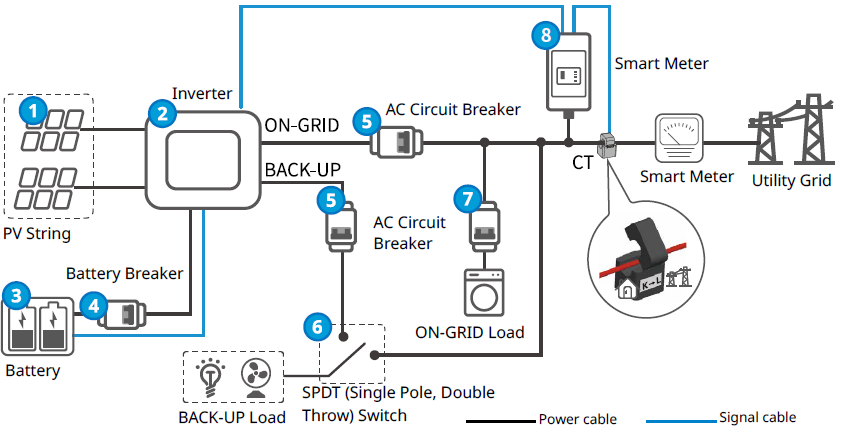
1. Các thành phần chính của một hệ thống Hybrid
Các thành chính của một hệ thống điện NLMT Hybrid
1. Các chuỗi pin NLMT
2. Hybrid Inverter
3. Battery (Pin lưu trữ)
4. CB DC của pin lưu trữ
5. CB AC của ngõ hòa lưới và ngõ dự phòng
6. Bộ chuyển nguồn tự động (ATS)
7. CB AC cho tải ở ngõ hòa lưới (tải thông thường)
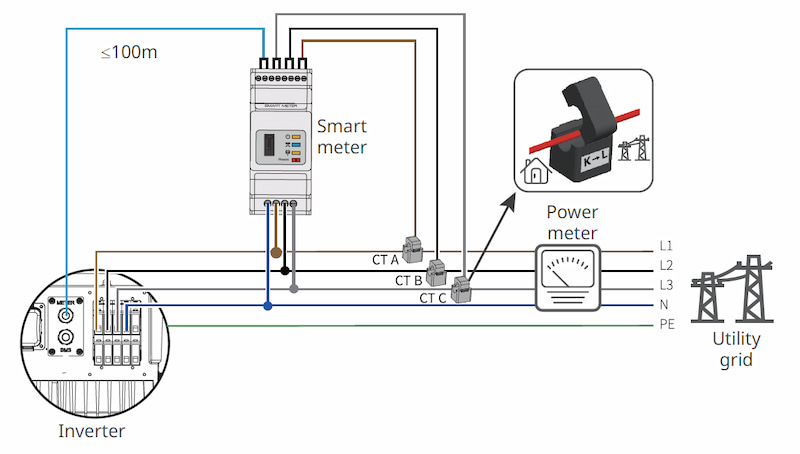
8. Smart Meter
2. Các lỗi thường gặp và phương án xử lý khi hệ thống lỗi
Trong quá trình sử dụng, đôi khi chúng ta sẽ gặp phải các tình huống lỗi khiến cho hệ thống điện NLMT không phát điện được.
Trước khi kiểm tra và xử lý lỗi của hệ thống, người xử lý phải có chuyên môn và nắm rõ về hệ thống. Cần xem lại các quy trình tắt, mở lại hệ thống để thao tác chính xác, đảm bảo quá trình bảo trì, bảo dưỡng hệ thống an toàn và hiệu quả. Quy trình tắt, bật lại hệ thống Hybrid tham khảo trong sách hướng dẫn sử dụng của sản phẩm hoặc liên hệ nhà cung cấp, đại lý để được hỗ trợ.
a) Lỗi mất lưới
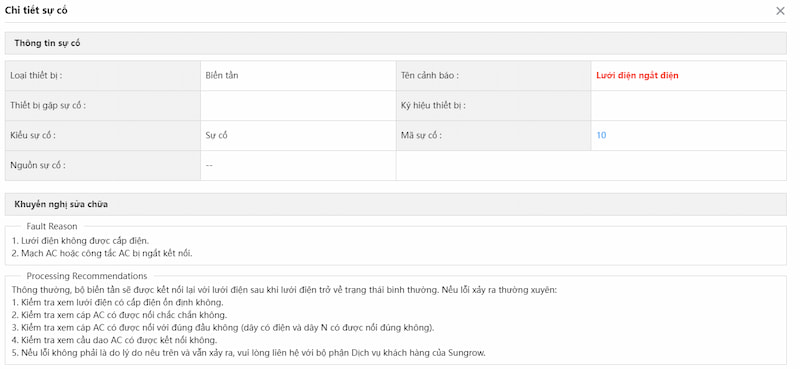
– Nguyên nhân:
- Điện lưới bị ngắt.
- MCB, MCCB cấp nguồn cho inverter đang ở trạng thái tắt hoặc bị hỏng.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra lại xem tại vị trí MCB, MCCB cấp nguồn cho inverter có điện áp không. Nếu điện lưới bị ngắt, inverter sẽ tự động khôi phục và hoạt động bình thường sau khi điện áp lưới trở lại bình thường.
- Kiểm tra xem liệu MCB, MCCB có bị hỏng không. Nếu hỏng thì cần thay thế MCB, MCCB cùng thông số.
- Kiểm tra nguyên nhân MCB nhảy.
b) Lỗi điện áp lưới (quá áp hoặc thấp áp)
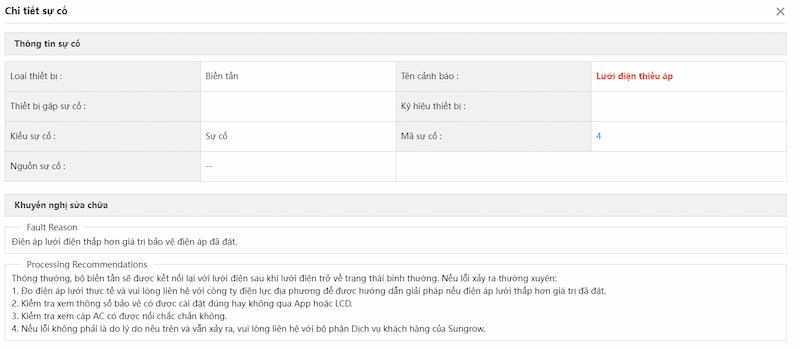
– Nguyên nhân:
- Điện áp lưới không nằm trong dải giá trị bảo vệ quá áp và thấp áp của inverter.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra xem điện áp lưới tại điểm đấu nối của biến tần có nằm trong dải cho phép hay không. Nếu điện áp cao hoặc thấp bất thường chỉ thoáng qua, inverter sẽ hoạt động trở lại sau khi giá trị điện áp lưới quay về ngưỡng hoạt động của inverter.
- Điều chỉnh giá trị bảo vệ điện áp bảo vệ của inverter để inverter hoạt động được với điện áp lưới hiện tại.
- Liên hệ điện lực địa phương để xử lý trong trường hợp điện áp lưới quá cao hoặc quá thấp.
c) Lỗi tiếp địa
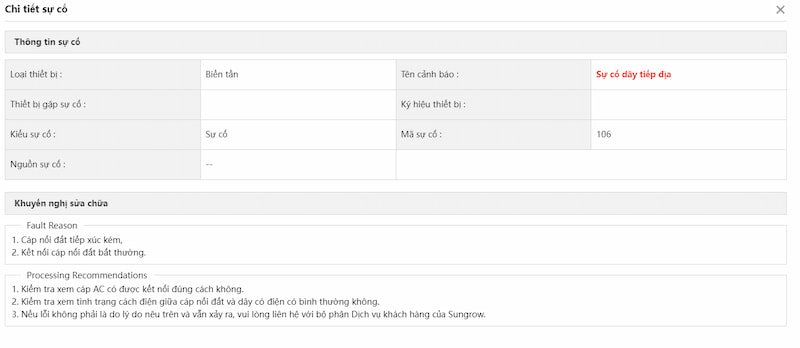
– Nguyên nhân:
- Cáp tiếp địa của inverter không được kết nối hoặc kết nối lỏng lẻo, không chắc chắn. Hệ thống Hybrid yêu cầu kết nối tiếp địa cả inverter, battery và tấm pin.
- Bãi tiếp địa không đảm bảo điện trở nối đất.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra lại cáp tiếp địa xem có bị đứt hay bị lỏng không.
- Kiểm tra lại điện trở nối đất của hệ thống tiếp địa.
d) Lỗi quá tải ngõ Back-up
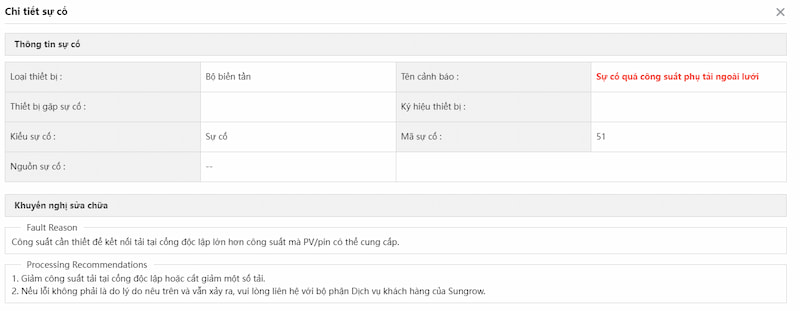
– Nguyên nhân:
- Công suất tải sử dụng ở ngõ Back-up vượt quá công suất ngõ Back-up của inverter.
- Sử dụng các tải ở ngõ Back-up có dòng khởi động lớn như: động cơ, bơm nước, điều hòa,….
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra tải kết nối: Kiểm tra các thiết bị đang kết nối vào ngõ Back-up của inverter và đảm bảo rằng tổng công suất của chúng không vượt quá giới hạn ngõ Back-up của inverter. Kiểm tra các tải ngõ Back-up có nằm trong danh sách hỗ trợ của nhà sản xuất hay không.
- Kiểm tra cài đặt của inverter: Xác định xem inverter có được cài đặt đúng không. Có thể cần điều chỉnh cài đặt để đảm bảo rằng nó có thể xử lý tải mà bạn đang sử dụng.
- Kiểm tra dây nguồn và bộ chuyển mạch tự động (ATS): Kiểm tra dây nguồn và bộ chuyển nguồn tự động để đảm bảo rằng chúng đang hoạt động đúng cách. Nếu có tải quá nặng, hãy tắt một số thiết bị để giảm tải.
- Tắt và khởi động lại hệ thống.
e) Lỗi truyền thông BMS giữa Inverter và Battery
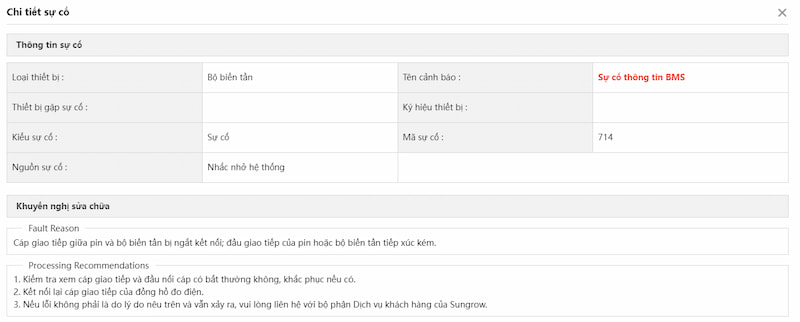
– Nguyên nhân:
- Dây cáp truyền thông giữa inverter và battery bị đứt, lỏng hoặc không được kết nối chắc chắn.
- Battery hoặc inverter bị hỏng không lên nguồn.
- Kết nối sai cổng truyền thông BMS CAN hoặc RS485.
- Sử dụng sai cáp kết nối truyền thông BMS, cáp không đúng chuẩn.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra cáp kết nối: Đảm bảo rằng cáp kết nối giữa inverter và BMS không bị đứt, hỏng hoặc kết nối không chắc chắn.
- Kiểm tra cài đặt truyền thông: Kiểm tra cài đặt truyền thông trên cả inverter và BMS để đảm bảo chúng đang sử dụng cùng một giao thức và tốc độ truyền thông.
- Kiểm tra điện áp và dòng tải: Đảm bảo rằng điện áp và dòng tải đang trong phạm vi hoạt động cho cả inverter và BMS. Nếu có sự không phù hợp, có thể gây lỗi truyền thông.
- Kiểm tra tình trạng pin lưu trữ: Kiểm tra xem liệu pin lưu trữ có đang hoạt động hay không. Nếu pin có vấn đề, BMS có thể không truyền thông được với inverter.
- Tắt và khởi động lại hệ thống.
f) Lỗi điện trở cách điện thấp và dòng rò
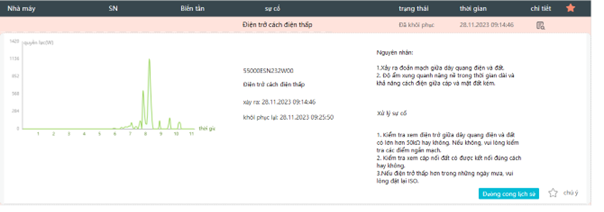
– Nguyên nhân:
- Dây cáp AC, DC lắp đặt trong môi trường ẩm ướt.
- Lớp vỏ cách điện của cáp AC, DC bị lão hóa hoặc bị xước làm giảm điện trở cách điện.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra điện trở cách điện AC, DC bằng máy đo điện trở cách điện.
- Thay thế dây cáp AC, DC nếu lớp vỏ bảo vệ có dấu hiệu lão hóa hoặc bị xước.
- Kiểm tra lại thiết bị chóng sét lan truyền SPD AC và DC.
g) Lỗi quá điện áp DC BUS
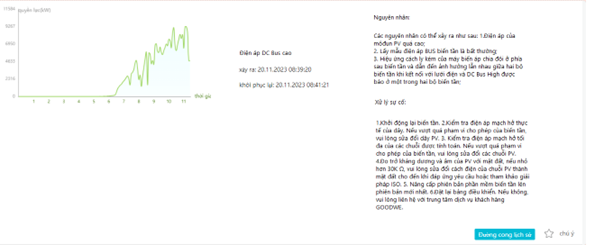
– Nguyên nhân:
- Điện áp chuỗi pin cao hơn dải điện áp hoạt động của inverter.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra lại chủng loại, điện áp tấm pin, số lượng tấm pin trên một chuỗi pin xem có phù hợp với dải điện áp hoạt động của inverter hay không. Nếu điện áp của chuỗi pin cao hơn điện áp hoạt động tối đa của inverter thì cần giảm số lượng tấm pin để điện áp chuỗi pin nằm trong dải điện áp hoạt động của inverter.
- Tắt và khởi động lại hệ thống.
h) Lỗi kết nối truyền thông Smart Meter
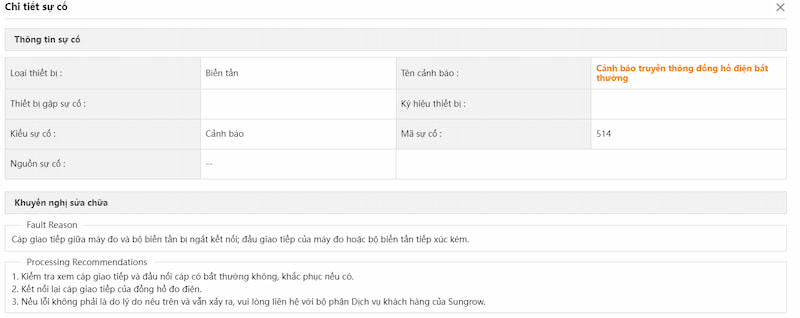
– Nguyên nhân:
- Dây cáp truyền thông giữa inverter và Smart meter bị đứt, lỏng hoặc không được kết nối chắc chắn.
- Smart meter hoặc inverter bị hỏng không lên nguồn.
- Sử dụng cáp không đúng chuẩn kết nối.
- Thông số truyền thông trên Smart meter cài đạt không chính xác.
– Cách xử lý:
- Kiểm tra cáp kết nối: Đảm bảo rằng cáp kết nối giữa inverter và Smart meter không bị đứt, hỏng hoặc kết nối không chắc chắn.
- Kiểm tra cài đặt truyền thông: Kiểm tra cài đặt truyền thông trên cả inverter và Smart meter để đảm bảo chúng đang sử dụng cùng một giao thức và tốc độ truyền thông.
i) Lỗi Smart Meter / CT ngược chiều
– Nguyên nhân:
- CT kẹp sai chiều.
- Pha kẹp CT không đúng với pha đo điện áp trên Smart meter.
– Cách xử lý:
- Xác định hướng mũi tên trên CT để kẹp đúng chiều. Lưu ý, mỗi hãng inverter có chiều CT khác nhau, vui lòng tham khảo sách hướng dẫn sử dụng của nhà sản xuất.
- Kiểm tra CT kẹp tương tứng với pha đấu nối điện áp đo đếm của Smart meter.
j) Lỗi sai thứ tự pha đầu vào
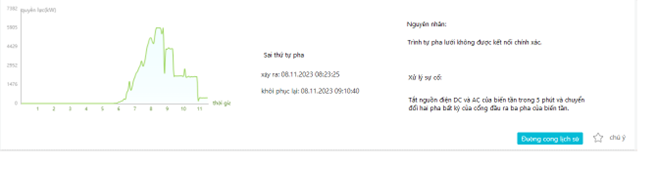
– Nguyên nhân:
- Sai thứ tự nguồn 3 pha đầu vào AC của inverter.
– Cách xử lý:
- – Kiểm tra lại thứ tự 3 pha tại vị trí đấu nối vào inverter bằng thiết bị kiểm tra thứ tự pha. Đấu nối lại cho đúng L1 L2 L3 N từ lưới vào L1 L2 L3 N tương ứng trên inverter.
- – Trong trường hợp không có thiết bị kiểm tra thứ tự pha, thực hiện đảo 2 trong 3 pha tại ngõ đấu nối AC của inverter cho đến khi inverter hết báo lỗi.
k) Lỗi relay ngõ hòa lưới / back-up
– Nguyên nhân:
- Relay ngõ hòa lưới hoặc ngõ Back-up đang có vấn đề.
– Cách xử lý:
- Tắt và khởi động lại hệ thống.
- Liên hệ nhà cung cấp hoặc đại lý để được hỗ trợ trong trường hợp inverter không thể khôi phục.
Đây là một số lỗi thường gặp trong quá trình vận hành hệ thống Hybrid trong thực tế. Nếu Quý Khách hàng, Quý Đối tác vẫn còn băn khoăn hoặc cần tư vấn thêm, hãy liên hệ ngay với DAT Group qua Hotline 1800 6567 (miễn phí cước) để được đội ngũ chuyên viên kỹ thuật am hiểu sâu về sản phẩm, giải pháp, công nghệ của chúng tôi tư hỗ trợ 24/7.